Zero Trust Security Model Explained
In our connected world today, many IT experts, security teams, and company leaders look for Zero Trust Security Model Explained. This is because old security methods do not keep up with new threats. What is zero trust? It is a new way to protect computers, data, and networks. The main rule is simple: do not trust anyone or anything automatically. You must check and verify every time someone or something tries to access your systems. This keeps bad actors out, even if they get past the first door.
People often ask what is zero trust security model. It changes the old idea of a big wall around your network. Now, you check inside and outside all the time. This helps with remote work, cloud tools, and mobile devices. Let’s break it down step by step in easy words.

aztechit.co.uk
Zero Trust vs Traditional Perimeter Security: What’s the Difference?
The History and Background of Zero Trust
The zero trust security model explained starts with its creation. John Kindervag, a researcher at Forrester, came up with the idea in 2010. He saw problems with old security. Back then, companies built a strong outside wall, like a castle moat. Once inside the wall, everyone got trust. They could move freely.
But hackers found ways in. Once inside, they caused big damage. Kindervag said: stop trusting inside too. Check every request, no matter where it comes from.
Over time, big groups like NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) made guides for it. In 2021, the US government told agencies to use Zero Trust. Many companies follow now because threats grow fast.
Zero trust security explained became popular with cloud use and remote jobs. During the pandemic, workers logged in from home. Old VPNs gave too much access. Zero Trust fixes that.
For a good overview, read this fromCloudflare’s glossary on what is Zero Trust1.
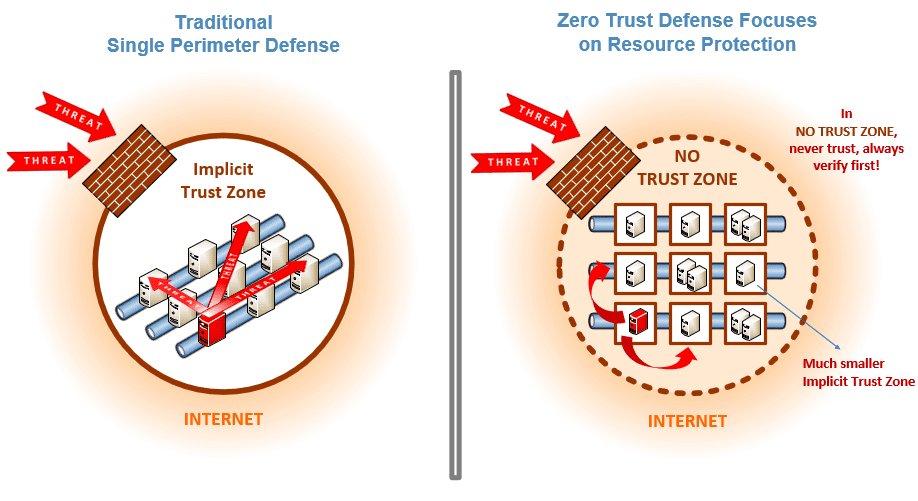
Why Old Security No Longer Works Well
Think of traditional security like a candy store with a lock on the front door. Once you open it and go in, you can take anything. Hackers love that. If they steal one key (like a password), they roam free.
Today, data is everywhere: in offices, clouds, phones, and home computers. Workers use personal devices. Partners connect from outside.
A breach happens often. Reports show over 80% of attacks use stolen credentials. Once in, hackers move side to side, called lateral movement.
What is zero trust security? It stops that movement. No big trust zone. Every door has its own lock and check.
Zero trust examples show big savings. Companies using it cut breach costs by a lot.
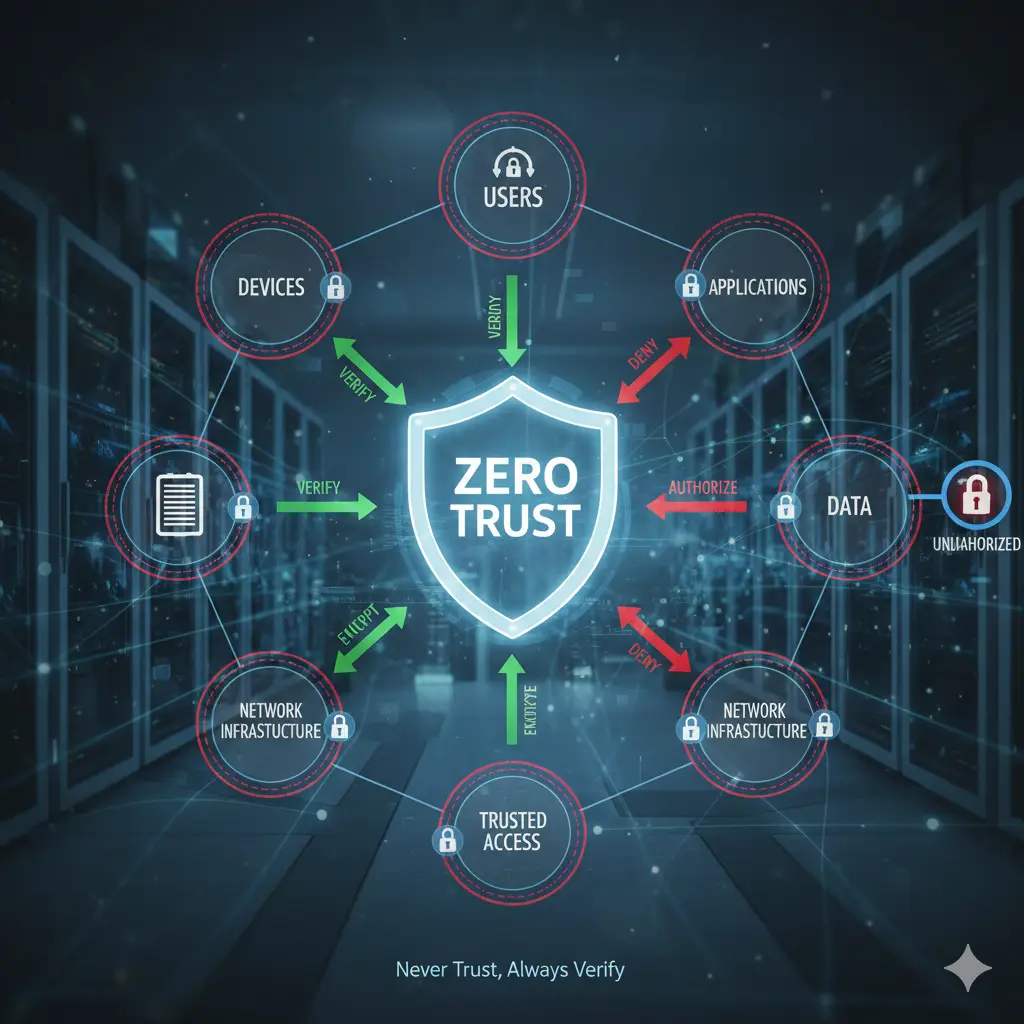
Core Principles of the Zero Trust Model
The principles of the zero trust model are easy to grasp. They guide everything.
Here they are in a list:
- Never Trust, Always Verify: Check who you are, what device you use, and why you need access. Do this every single time.
- Use Least Privilege: Give only the smallest access needed. For example, if you need one file, don’t give the whole folder.
- Assume Breach: Plan as if a hacker is already inside. Make it hard for them to spread.
- Microsegmentation: Split your network into small parts. Like rooms with locked doors. A break in one room stays there.
- Continuous Monitoring: Watch all activity all the time. Use tools to spot strange things fast.
These make the ‘zero trust’ security model strong and flexible.
Zero trust security explained principles of the zero trust model often uses these as the base.
nist.gov
Zero Trust Cybersecurity: ‘Never Trust, Always Verify’ | NIST
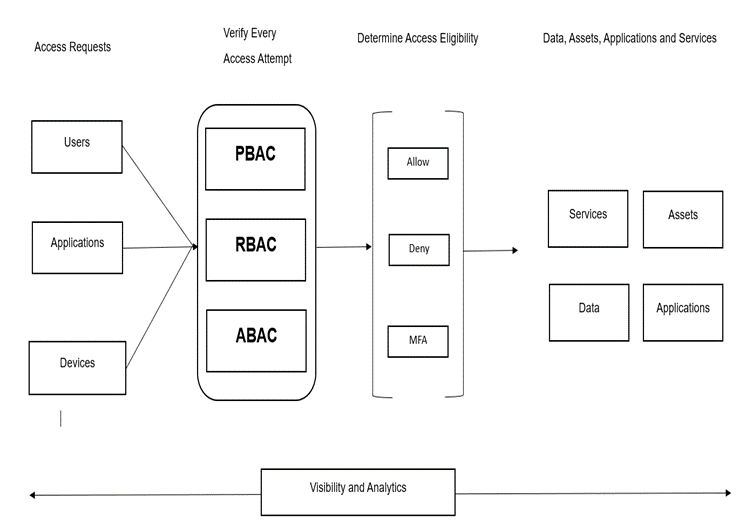
Main Parts of Zero Trust Architecture
A zero trust architecture diagram helps see the big picture. It has key parts that work together.
- Identity Verification: Use strong ways to prove who you are. Like passwords plus phone codes (MFA).
- Device Checks: Make sure the device is safe, updated, and not hacked.
- Network Controls: Encrypt data and use small segments.
- Application Security: Protect apps and only allow needed access.
- Data Protection: Lock data with rules, no matter where it goes.
- Automation and Analytics: Use AI to watch and respond fast.
Zero trust technology includes tools like ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access). This is better than old zero trust vpn. VPNs open the whole network. ZTNA opens only one app.
Many like zero trust cloudflare for easy web protection.
securdi.com
Zero Trust Architecture: Key Components and Considerations
Big Benefits of Using Zero Trust
Zero trust security model explained in cyber security shows many pluses.
- Better protection from breaches. Limits damage if someone gets in.
- Safer remote work. No need for risky VPNs.
- Meets rules and standards easily, like NIST.
- Saves money over time. Fewer big attacks mean less cost.
- Works well with cloud and hybrid setups.
- Gives clear views of who accesses what.
Stats: Companies with Zero Trust see 50% fewer incidents, per some reports.
There is no commonly used model for zero trust security that fits all exactly. You tailor it.
Step-by-Step Guide to Start Zero Trust
You can build it slowly. Here is a clear plan for zero trust presentation or real use.
- Get Leaders on Board: Explain why. Show risks of old ways.
- Map Everything: List all data, apps, users, and devices. Know your “protect surface.”
- Set Strong Policies: Decide rules for access. Use least privilege.
- Add Verification Tools: Start with MFA everywhere.
- Segment Your Network: Create small zones.
- Monitor and Log: Set up tools to watch activity.
- Automate Where Possible: Let systems handle checks.
- Train Your Team: Teach everyone the new ways.
- Test Often: Run fake attacks to check.
- Grow Step by Step: Start with one part, like email, then add more.
This roadmap helps IT teams and leaders.
For more steps, seeIBM’s topics on Zero Trust2.
Real-Life Examples of Zero Trust
Many big companies use it.
- Google’s BeyondCorp: Started years ago. Employees access work from any device, anywhere. No VPN. Check context each time.
- Microsoft: Uses Zero Trust for its own systems and offers tools for others.
- Governments: US federal agencies follow mandates.
- Zero trust examples: A bank stopped a ransomware spread with segments.
These show what is the zero trust security model in action.
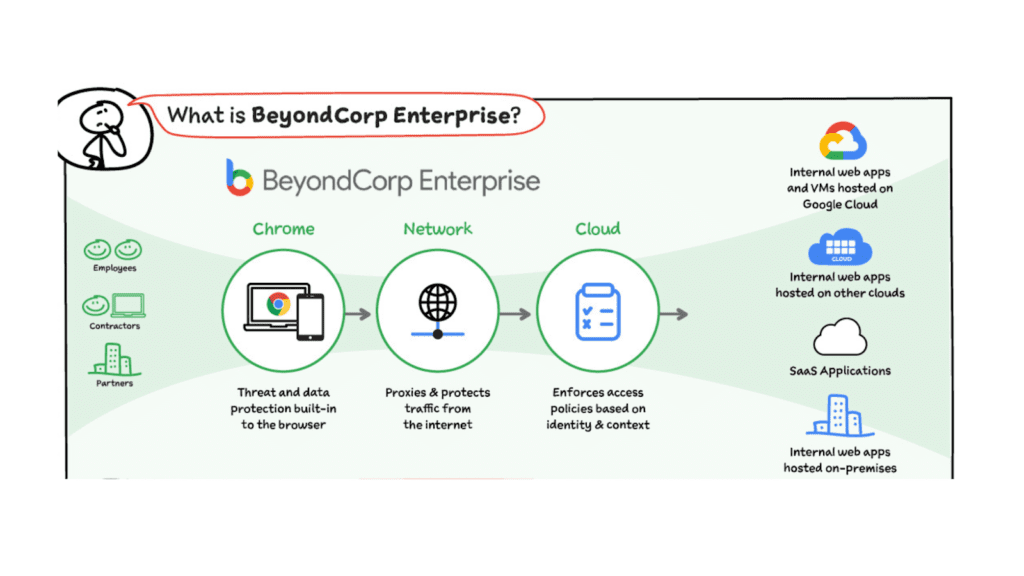
cloud.google.com
Zero Trust and BeyondCorp Google Cloud | Google Cloud Blog
Learn details fromCrowdStrike’s Zero Trust page3.
Common Challenges and Easy Fixes
Change can be hard.
- It takes time to set up.
- Users may complain about extra checks.
- Costs for new tools.
Fixes:
- Start small to show wins fast.
- Choose tools that fit your current setup.
- Train people and explain why it’s safer.
- Get help from experts if needed.
Most find it worth it.
Tools You Can Use for Zero Trust
Many options exist.
- Identity tools like Okta or Azure AD.
- Network tools from Palo Alto or Zscaler.
- Endpoint protection from CrowdStrike.
Pick based on your size and needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Zero Trust Security Model Explained in simple terms?
The Zero Trust Security Model Explained means you never trust anyone or anything automatically. You always check and verify every time someone tries to access data or systems. It keeps things safe in today’s world with clouds and remote work.
What is zero trust security?
What is zero trust security? It is a way to protect networks by checking everything all the time. No big trust inside the network. Verify identity, device, and reason for access each time.
How does Zero Trust differ from old VPNs?
Old zero trust vpn setups give full network access once you log in. Zero Trust gives only what you need, like one app. It is safer and stops hackers from moving around.
What are the main principles of the zero trust model?
The principles of the zero trust model include: never trust, always verify, use least privilege, assume breach, and monitor everything. These keep damage small if something goes wrong.
Is there one common model for everyone?
There is no commonly used model for zero trust security that fits all companies exactly. You adapt it to your needs, using guides like NIST.
Why do companies use Zero Trust now?
With more remote work and cloud tools, old walls don’t protect well. Zero trust security explained helps stop big breaches and meets new rules.
Can small teams or companies use Zero Trust?
Yes! Start with easy steps like adding MFA (multi-factor authentication) and basic checks. Grow from there.
Conclusion: Make Zero Trust Part of Your Plan
To wrap up, the Zero Trust Security Model Explained is about always checking and never assuming trust. It uses simple principles like verify everything and least privilege. In today’s world with clouds and remote teams, it gives strong protection.
IT pros, leaders, and companies changing digitally find it helpful. Start small, follow steps, and see better safety.
What part of your security will you check with Zero Trust ideas first?
References
- Cloudflare Learning: What is Zero Trust? – Easy explanations, comparisons, and practices; suits engineers and teams starting out (focus on real tools and examples). ↩︎
- IBM Think Topics: Zero Trust – Covers history, pillars, and enterprise strategies; great for leaders and architects planning big changes (includes stats and NIST ties). ↩︎
- CrowdStrike Cybersecurity 101: Zero Trust Security – Breaks down principles, steps, and threat stops; targets pros fighting daily attacks (strong on automation and cases). ↩︎





