Open Source vs Proprietary Software: A Clear and Simple Guide
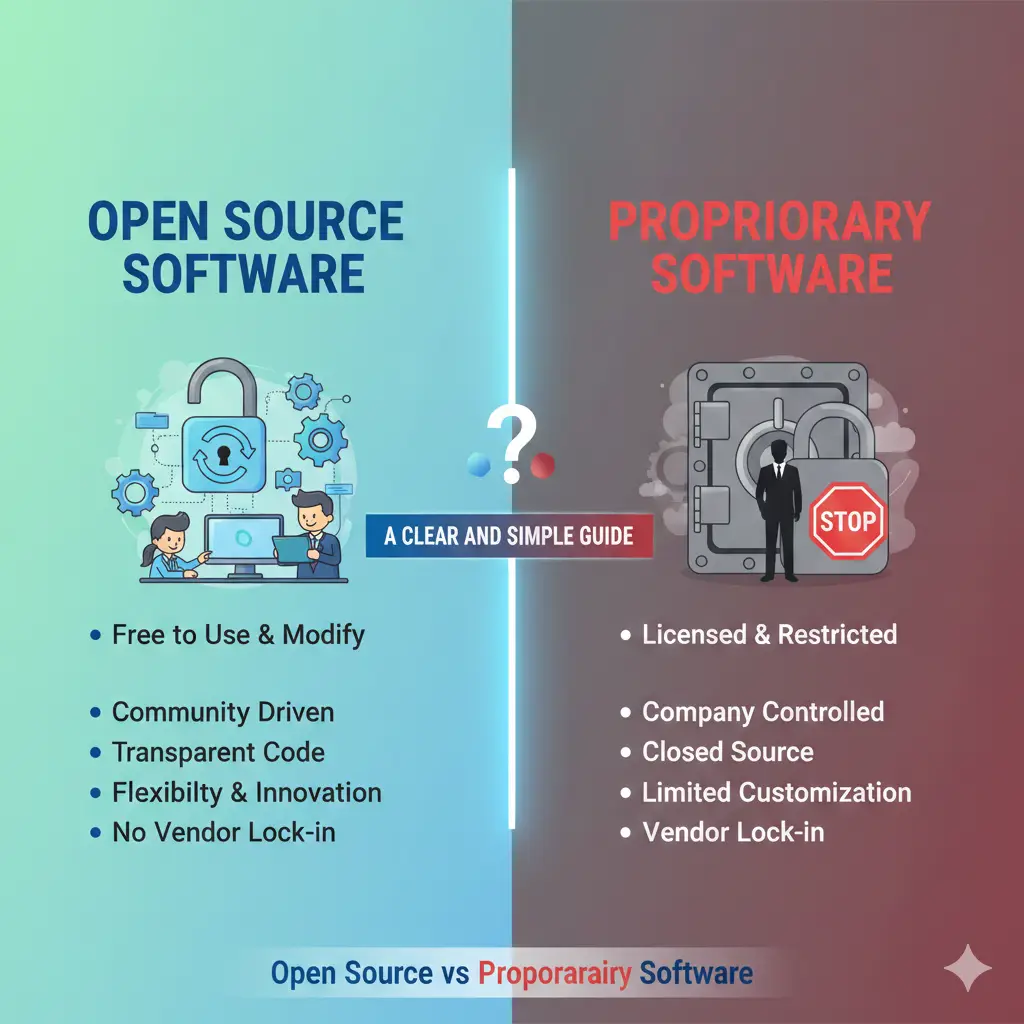
People often look for information on Open Source vs Proprietary Software because they want to make good choices about the tools they use. This topic helps everyone from students learning basics to business owners picking software for their teams. In easy words, open source software is free and lets anyone see or change the code. Proprietary software costs money and keeps the code secret, owned by a company. As we explore Open Source vs Proprietary Software today in 2025, many reports show that almost all companies use open source in some way. For example, 97% of apps have open source parts. This guide breaks it down step by step with simple explanations, examples, and pictures to help you understand better.

A Guide to Evaluating Open Source versus Proprietary Software for …
This chart shows a simple comparison of open source and proprietary software, like a continuum to help you see the differences clearly.
What Does Open Source Software Mean?
Open source software is like a recipe that everyone can see and improve. The code – the instructions that make the software work – is open for all. People from anywhere in the world can look at it, use it, fix bugs, or add new features. You do not pay to use it most of the time.
This idea started many years ago when programmers wanted to share their work freely. Today, big communities build and maintain these tools.
Here are some popular open source vs proprietary software examples from the open source side:
- Linux: A free operating system that runs on many computers and servers.
- Firefox: A web browser you can use instead of others.
- Android: The system on most phones, based on open code.
- VLC: A player for videos and music that works on everything.
- LibreOffice: Free tools for writing documents, spreadsheets, and slides.
These tools are loved because they are free and flexible..
Many students start learning with open source because they can see the code and practice changing it.
What Does Proprietary Software Mean?
Proprietary software is the opposite. The company that makes it keeps the code secret. You buy a license to use it, like renting the right to run it on your computer. You cannot change the code or share it freely.
Companies make proprietary software to protect their ideas and make money from sales or subscriptions.
Common examples include:
- Microsoft Windows: The operating system on many PCs.
- macOS: Apple’s system for Macs.
- Microsoft Office: Word, Excel, PowerPoint.
- Adobe Photoshop: For editing photos.
- QuickBooks: For business money tracking.
These are known for being easy to use right away and having good help from the company.

IT Support
Company support team helping customers – this is a big plus for proprietary software users.
Main Differences in Open Source vs Proprietary Software
Let’s look at the big differences. Many people search for open source vs proprietary software advantages disadvantages to see this side by side.
Here is an easy table to compare:
| Feature | Open Source Software | Proprietary Software |
| Code Access | Anyone can see and change it | Only the company sees and changes it |
| Cost | Mostly free | You pay for license or subscription |
| Customization | Very easy to modify | Hard or not allowed |
| Support | From community forums and volunteers | From paid company team |
| Security | Many people check for problems | Company experts check |
| Updates | Community adds them quickly | Company plans and releases them |
| Reliability | Depends on community activity | Usually very stable |
You can see more details in this helpful comparison fromGeeksforGeeks1.
Both types have open source software and proprietary software similarities too. They both aim to work well, be safe, and help users get things done. The way they are made and shared is what differs most.
A clear difference chart between open source and proprietary software – helps visualize the key points.
Advantages of Open Source Software
Open source has many good points. Here are the main advantages:
- It is free, so you save money.
- You can change it to fit exactly what you need.
- Bugs get fixed fast because many people look at the code.
- No lock-in – you can switch or fork it if needed.
- It builds trust because the code is open.
- Great for learning – students and developers practice on real code.
In 2025, open source powers most of the internet. Servers, clouds, and AI tools use it a lot.
One big plus is innovation. Anyone can add ideas. For example, Linux started small but now runs supercomputers.
Open source ecosystem – shows how many parts connect and grow together through collaboration.
For developers, this means more jobs and skills. Many companies hire people who know open source tools.
Disadvantages of Open Source Software
Nothing is perfect. Open source has some downsides:
- You might need tech skills to install or fix it.
- Support is from online forums, not a phone call to a team.
- Some projects stop if volunteers lose interest.
- Security can be a risk if not many people watch it.
But active projects like Linux are very safe.
Advantages of Proprietary Software
Now, let’s talk about advantages of proprietary software:
- It is easy to use with nice designs.
- You get official support from experts.
- Updates come regularly with new features.
- It often works well with other products from the same company.
- Strong focus on security from paid teams.
For businesses that need reliability, this helps a lot. No worry about sudden changes.

The Ultimate Guide to Developing a Proprietary App
Team discussing proprietary tools – like how companies build and support their software.
Many big offices use Microsoft tools because everyone knows them.
Proprietary software advantages and disadvantages often come up in talks. The advantages shine for quick setup and help.
Disadvantages of Proprietary Software
Here are the main proprietary software disadvantages:
- It costs money, sometimes a lot over time.
- You cannot change the code.
- Vendor lock-in – hard to switch to something else.
- Updates depend on the company, which might be slow.
- Less transparent – you trust the company fully.
These can be big issues for growing businesses.
How Students and Beginners Can Use This Comparison
If you are a student, Open Source vs Proprietary Software is a key topic in classes. Open source helps you learn by seeing real code. You can download Linux and try it for free.Many schools use open tools like Python, which is open source.
For exams or open source vs proprietary software ppt projects, use simple charts like the ones here. Explain with examples from daily life.Student coding and learning software engineering – perfect for beginners exploring open source.
Start with free tools to build skills without spending money.
Tips for Developers and Technical Teams
Developers often mix both. Use open source for backend like databases (PostgreSQL is open, better than some paid ones).
For front end, proprietary like Adobe for design.
On forums like open source vs proprietary software reddit, developers share stories. Many say open source gives freedom in coding.
In 2025, AI tools like open models will grow fast.
Open Source vs Proprietary Software for Startups and Businesses
Startups love open source to save cash and move fast. You can customize without waiting for a company.
Read more about this in theHeavybit articl2e.
Big companies use proprietary for important parts needing strong support.
Many choose hybrid – open for most, proprietary for special needs.
Stats: 96% of organizations plan to keep or add more open source.
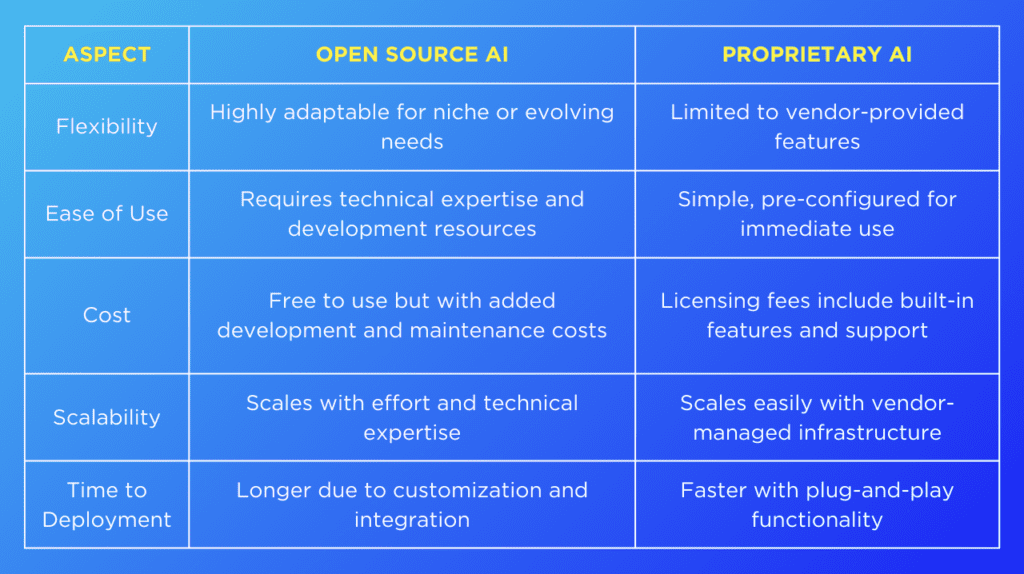
Open Source vs Proprietary AI: Choose the Right Solution | SmartDev
Startup team choosing between open source and proprietary options – a common decision in 2025.
Founders look at long-term costs. Open source often wins for growth.
For more business views, check theNebius blog3.
Real-Life Examples
Let’s see open source vs proprietary software examples in action:
- Phones: Android (open base) vs iOS (proprietary).
- Browsers: Chrome (parts open) vs Safari (proprietary).
- Editing: GIMP (open, free) vs Photoshop (paid).
Governments in many countries push open source for safety and savings.
Cloud services like AWS use lots of open source inside.
Trends to Watch in 2025 and Beyond
In 2025, open source leads in AI and cloud. Companies contribute to open projects to make them better.
Security is big – both types improve, but open source gets quick community fixes.
More hybrids appear, like open core where base is free, extras paid.
Tech fans debate philosophy: freedom vs control.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choose the Right Software
Here is how to decide:
- Look at your budget – open source if low.
- Check needed features – proprietary if specific polish.
- Think about team skills – open if you can handle setup.
- Plan support – proprietary for fast help.
- Test both – many have free versions.
- Consider future growth – open for easy scaling.
- Read reviews and stats.
Most people end up using a mix for the best results.
Frequently Asked Questions About Open Source vs Proprietary Software
What is the main difference in Open Source vs Proprietary Software?
The biggest difference is the code. In open source, anyone can see, use, and change the code for free. In proprietary, the company keeps the code secret and you pay to use it. This affects cost, flexibility, and support.
Which one is cheaper: open source or proprietary?
Open source is usually free. You do not pay for the software itself. Proprietary software costs money for licenses or subscriptions. This is a big part of open source vs proprietary software advantages disadvantages.
What are the advantages of proprietary software?
Advantages of proprietary software include easy use, professional designs, and official support from the company. You get quick help and regular updates planned by experts.
Is open source better for students and learning?
Yes! Students love open source because they can see the code and learn from it. It is free, so schools and beginners use it a lot.
Are there similarities between open source and proprietary software?
Yes, open source software and proprietary software similarities include making tasks easier, needing updates, and focusing on security.
What are proprietary software disadvantages?
Proprietary software disadvantages include high costs, no code changes, and vendor lock-in – hard to switch later.
Can I use both types together?
Yes! Many people and companies mix them. Use open source for flexible parts and proprietary for supported tools.
Conclusion: Making the Best Choice in Open Source vs Proprietary Software
In the end, Open Source vs Proprietary Software both have strong points that fit different needs. Open source offers freedom, no cost, quick fixes, and great learning chances. It suits students, developers, startups, and anyone who wants flexibility. Proprietary gives easy use, pro support, and stable features – good for businesses needing quick help and polish. In 2025, most experts use a mix of both for the best outcome. Reports show huge growth in open source, but proprietary still holds key spots. Think about your goals, budget, and team to pick what works for you.
Which one do you use more in your daily work or studies, and what do you like about it?
References
- GeeksforGeeks: Difference Between Open Source and Proprietary Software – Simple tables and basics; great for students and beginners to learn definitions fast. ↩︎
- Heavybit: Open-Source vs Proprietary Software – Strategy tips for startups; targets founders and IT managers on licensing and growth. ↩︎
- Nebius Blog: Open-Source vs Proprietary – Real pros/cons with business examples; helps developers and CTOs think about costs and customization. ↩︎